CHAPTER OVERVIEW:
Story of Belgium
Belgium is a small country in Europe with a population of over 1 crore, about half the population of Haryana. Of the country’s total population, 59% speaks Dutch language, 40% of people speak French and the remaining 1% speak German. Look at the map below to know the language variation of Belgium. The minority French-speaking community was rich and powerful, so they got the benefit of economic development and education. This created tensions between the Dutch-speaking and French-speaking communities during the 1950s and 1960s.
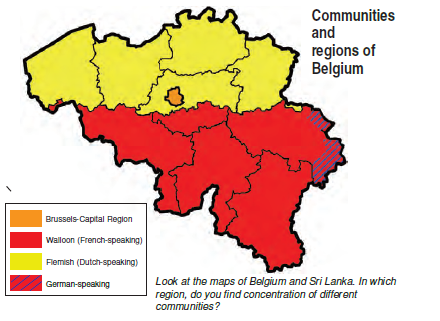
Accommodation in Belgium
In Belgium, the government handled the community difference very well. Between 1970 and 1993, Belgian leaders amended their constitution four times and came up with a new model to run the government.
Here are some of the elements of the Belgian model.
- The Constitution prescribes that the number of Dutch and French-speaking ministers shall be equal in the Central Government. Some special laws require the support of the majority of members from each linguistic group. Thus, no single community can make decisions unilaterally.
- The state governments are not subordinate to the Central Government.
- Brussels has a separate government in which both communities have equal representation.
- Apart from the Central and the State Government, there is a third kind of government. This ‘community government’ is elected by people belonging to one language community – Dutch, French and German-speaking – no matter where they live. This government has the power regarding cultural, educational and language-related issues.
The Belgium model was very complicated but it helped to avoid civic strife between the two major communities.
Story of Sri Lanka
Now, let’s take the situation of another country, Sri Lanka. It is an island nation having a population of 2 crores, about the same as in Haryana. Sri Lanka has a diverse population. The major social groups are the Sinhala-speakers (74%) and the Tamil-speakers (18%). Among Tamils, there are two subgroups, “Sri Lankan Tamils” and “Indian Tamils”. You can see the map below to know the population distribution of different communities of Sri Lanka.
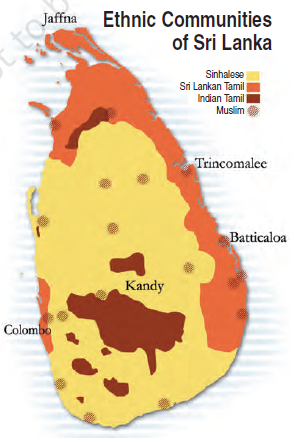
In Sri Lanka, the Sinhala community enjoyed the bigger majority and imposed its will on the entire country.
Majoritarianism in Sri Lanka
Sri Lanka emerged as an independent country in 1948. The Sinhala community was in the majority so they had formed the government. They also followed preferential policies that favoured Sinhala applicants for university positions and government jobs. These measures taken by the government gradually increased the feeling of alienation among the Sri Lankan Tamils. Sri Lankan Tamils felt that constitution and government policies denied them equal political rights, discriminated against them in getting jobs and other opportunities and ignored their interests. Due to this, the relationship between the Sinhala and Tamil communities become poor. Sri Lankan Tamils launched parties and struggles for the recognition of Tamil as an official language, for regional autonomy and equality of opportunity in securing education and jobs. But their demand was repeatedly denied by the government. The distrust between the two communities turned into widespread conflict and turned into a CIVIL WAR. As a result, thousands of people of both the communities have been killed. Many families were forced to leave the country as refugees and many more lost their livelihoods. The civil war ended in 2009 and caused a terrible setback to the social, cultural and economic life of the country.
What have you learned from the Stories of Belgium and Sri Lanka?
- Both countries are democracies but they dealt differently with the concept of power sharing.
- In Belgium, the leaders have realised that the unity of the country is possible only by respecting the feelings and interests of different communities and regions. This resulted in mutually acceptable arrangements for sharing power.
- Sri Lanka shows that, if a majority community wants to force its dominance over others and refuses to share power, it can undermine the unity of the country.
Why is power sharing desirable?
You will find the answer to this question in the points below.
- Power sharing is good because it helps to reduce the possibility of conflict between social groups.
- The second reason is that, a democratic rule involves sharing power with those affected by its exercise, and who have to live with its effects. People have a right to be consulted on how they are to be governed.
Let us call the first set of reasons Prudential and the second moral. The prudential reasons stress that power sharing will bring out better outcomes, whereas the moral reasons emphasise the act of power sharing as valuable.
Form of Power Sharing
Most of you must think that Sharing power = dividing power = weakening the country. A similar thing was believed in the past. It was assumed that all the power of a government must reside in one person or group of persons located at one place. Otherwise, it would be very difficult to make quick decisions and to enforce them. But these notions have changed with the emergence of democracy. In a democracy, people rule themselves through institutions of self-government. Everyone has a voice in the shaping of public policies. Therefore, in a democratic country, political power should be distributed among citizens.
In modern democracies, power sharing can take many forms, as mentioned below:
- Power is shared among different organs of government, such as the legislature, executive and judiciary. This is called horizontal distribution of power because it allows different organs of government placed at the same level to exercise different powers. Such separation ensures that none of the organs can exercise unlimited power. Each organ checks the others. This arrangement is called a system of checks and balances.
- Power can be shared among governments at different levels – a general government for the entire country and governments at the provincial or regional level which is called federal government.
- Power may also be shared among different social groups such as the religious and linguistic groups. ‘Community government’ in Belgium is a good example of this arrangement. This method is used to give minority communities a fair share in power.
- Power sharing arrangements can also be seen in the way political parties, pressure groups and movements control or influence those in power. When two or more parties form an alliance to contest elections and if they get elected, they form a coalition government and thus share power.
RELATED VIDEO:

Comments
Post a Comment